Introduction to the AWS CLI
There are three methods to upload and download data to Amazon Web Services. You can use the command line (CLI), AWS SDK, or the S3 REST API. In this article, we will explore the command Line interface, and the most common commands to manage an S3 bucket.
The maximum size of a file that you can upload by using the Amazon S3 console is 160 GB. The maximum bucket size is 5TB. You can not use s3api on files uploads larger than 5GB. Command line tools can achieve upload speeds greater than 7 MB’s. But, you can go even faster if you turn on acceleration. It is not recommended because an additional cost will be incurred.
Common switches
- –dryrun = test what files would be uploaded, prior to running command.
- — summarize = include a total at the bottom of the output.
- — human-readable = show files sizes in Gb and not Bytes.
- –output text = format the output on separate lines
- –content-type=text/plain = Tell aws the upload data is text data (not video or other).
- –recursive = show full file path
- –exclude – leave out certain files.
- –include = include certain files.
- –delete = this flag is needed to remove any files.
- –meta-data = Use this flag to upload custom data like the true MD5 hash
List contents of a bucket
aws s3 ls s3://bucket1/directory1/directory2/ --summarize --human-readable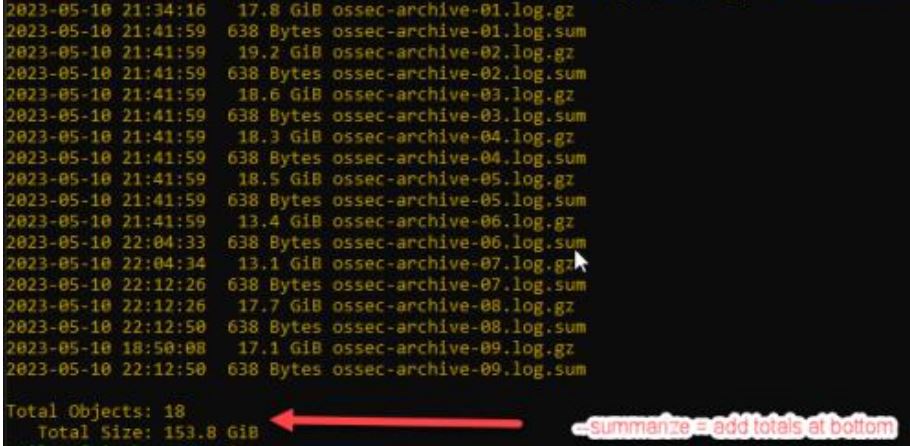
Copy a single file
If the file is large, the cp command will automatically handle a multi-part upload dynamically. If the full path is not present, it will create it automatically in the s3 bucket.
aws s3 cp ~/test.txt s3://bucket1/dir1/dir2/ --human-readable Copy multiple files from a local directory
There are two commands that can be used to copy multiple files. Use sync or cp with the –recursive switch.
aws s3 sync ./test/May s3://bucket1/May/ --human-readable --summarizeOR
aws s3 cp ./test/May s3://bucket1/May/ --recursive --content-type=text/plainCopy only files with .sum extension
aws s3 sync ~/dir1/ s3://bucket1/dir1/ --exclude '*' --include '*.sum' --dryrun Copy a directory and exclude two files
aws s3 sync ~/dir1/ s3://bucket1/dir1/ --exclude 'file1.txt' --exclude 'file2.txt'