Understanding Time
Time is a critical component of every computer. When to run updates, launch scheduled tasks, or just to keep user’s informed, are all dependent on time.
Every computer has a built in clock on the motherboard, usually powered by a battery, to keep track of the time. This hardware based clock is called the Real Time Clock (RTC) and is used to power the human readable ‘system time’, based on time zones.
- System Time = Uses Time Zones
- RTC = Real Time Zone = Uses Hardware clock
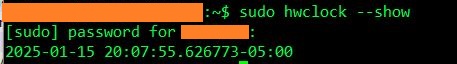
Unfortunately, the hardware clock will always eventually get out of sync with real time and need to be adjusted. This occurs because of power outages, battery on the MB dies, or other reasons.
Ubuntu Settings
Two commands are used to control the date and time. First, the ‘timedatectl‘ command is used to set the time zone. Next, the ‘timesyncd‘ command is used start or stop the sync service and to turn on or off the network time protocol (NTP).
An older process to manage these functions is called ntpd. While this process is still supported, it is recommended to use the newer methods.
Check Your Time Zone
In the United States, there are three primary time zones.
- UTC (Universal Time Coordinated)
- EDT (Eastern Daylight Time) = 2nd Sunday March to 1st Sunday in Nov. = 4 hr behind UTC
- EST (Eastern Standard Time) = 1st Sunday Nov to 2nd Sunday March. = 5 hr behind UTC
date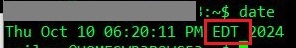
Get a list of available time zones
timedatectl list-timezonesChange the Time Zone
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/New_YorkCheck the Sync & NTP Services
Note: Typically, the Real Time Clock or ‘RTC in local TZ’ should always be set to ‘no’. This is due to that most of the US uses spring/fall time changes and the RTC does not know anything about that.
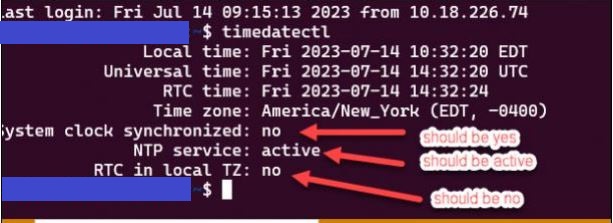
Turn on the ‘System clock synchronized’
Check that there is a name server or two listed in the configuration file. The entries should be space separated.
sudo vim /etc/systemd/timesyncd.confAdd the following lines under [Time]:
NTP=ntp.myserver.com time.nist.gov
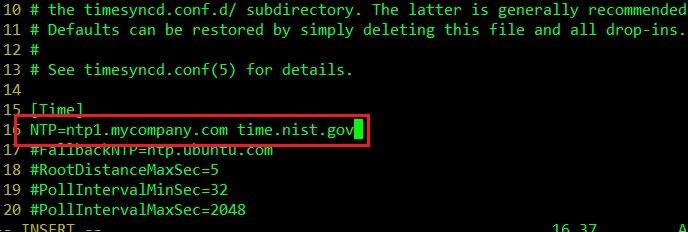
Next, run the below command.
sudo systemctl start systemd-timesyncdTurn on the ‘NTP Service’
sudo timedatectl set-ntp onVerify the Clock is Synced
systemctl status systemd-timesyncd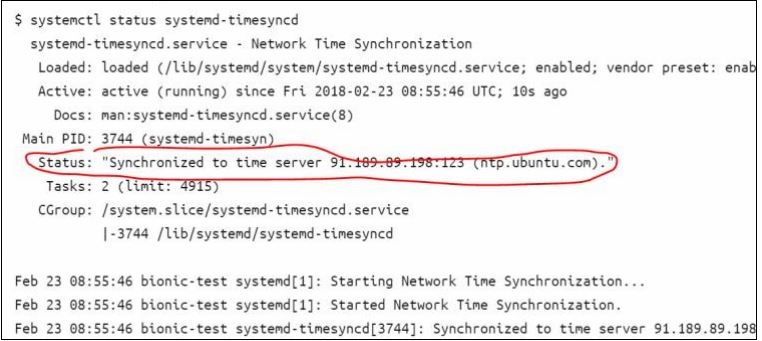
Ref: https://www.linuxfordevices.com/tutorials/ubuntu/set-up-time-synchronization-ubuntu
Ref: https://opensource.com/article/20/6/time-date-systemd
Ref: https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/about-time-synchronisation
